Your skin serves as your body’s first line of defense against the outside world, protecting internal organs while regulating temperature and providing sensory information about your environment. As the largest organ in the human body, skin deserves careful attention and regular monitoring to maintain its health and detect potential problems early. Understanding how to care for your skin and recognize warning signs can literally be life-saving, making skin health awareness an essential component of overall wellness.
Understanding Your Skin: More Than Just a Protective Barrier
Human skin is a remarkably complex organ system that performs numerous vital functions beyond simple protection. It consists of multiple layers, each with specific roles that contribute to overall health and well-being. The epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layers work together to create a sophisticated barrier that adapts to environmental conditions while maintaining internal stability.
The epidermis contains melanocytes, specialized cells that produce melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color and natural protection against ultraviolet radiation. These cells can sometimes develop abnormalities that lead to various types of skin growths, some benign and others potentially dangerous.
Understanding the normal appearance and behavior of your skin provides the foundation for recognizing when changes occur that might warrant medical attention. Skin naturally varies in texture, color, and thickness across different body areas, and these variations are typically normal and expected.
Regular self-examination helps establish familiarity with your skin’s normal patterns, making it easier to notice when something appears different or concerning. This baseline knowledge becomes invaluable for early detection of potential problems.
The skin’s appearance changes naturally with age, sun exposure, and various environmental factors, but understanding which changes are normal versus those that require attention is crucial for maintaining good health.
The Spectrum of Skin Growths: From Harmless to Concerning
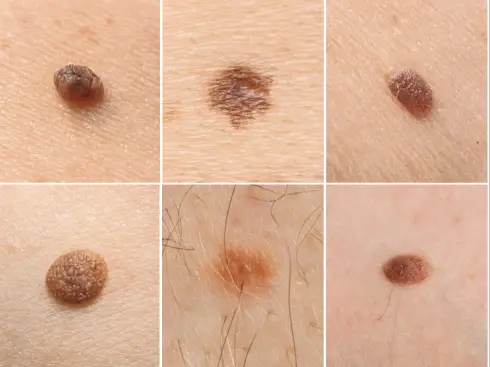
The human body commonly develops various types of skin growths throughout life, most of which are completely harmless and require no treatment. However, understanding the different types of growths and their characteristics helps distinguish between normal skin changes and those that might indicate more serious conditions.
Benign growths include freckles, age spots, seborrheic keratoses, and most moles, which typically remain stable in appearance over time. These growths may vary in size, color, and texture but generally don’t pose health risks unless they become irritated or infected due to friction or injury.
Precancerous lesions represent an intermediate category where cells show abnormal changes that could potentially develop into cancer if left untreated. These growths often result from cumulative sun damage and typically respond well to treatment when detected early.
Malignant growths require immediate medical attention and treatment to prevent spreading to other parts of the body. Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes and survival rates for all types of skin cancer.
The key to maintaining skin health lies in understanding these different categories and knowing when to seek professional evaluation for concerning changes or new growths.
Risk Factors: Understanding Your Personal Skin Cancer Risk
Multiple factors influence an individual’s risk of developing skin cancer, with some being modifiable through lifestyle choices while others are determined by genetics and personal history. Understanding these risk factors helps inform prevention strategies and screening recommendations.
Fair skin, light-colored eyes, and blonde or red hair increase skin cancer risk due to lower levels of protective melanin. However, people of all skin types can develop skin cancer, making awareness important for everyone regardless of complexion.
Family history of skin cancer significantly increases personal risk, as genetic factors influence how skin responds to environmental damage and how effectively cellular repair mechanisms function. Individuals with family history should be particularly vigilant about prevention and screening.
Personal history of severe sunburns, especially during childhood, substantially increases lifetime skin cancer risk. The cumulative effects of sun damage can manifest decades after the initial exposure, making prevention important at every age.
Occupational or recreational activities that involve significant sun exposure increase risk, particularly for individuals who work outdoors or participate in activities like boating, skiing, or golf that involve extended time in reflective environments.
Immunosuppression due to medications, medical conditions, or treatments can increase skin cancer risk by reducing the body’s ability to detect and destroy abnormal cells before they become problematic.
Prevention Strategies: Your First Line of Defense
Effective skin cancer prevention involves multiple strategies that work together to minimize exposure to harmful ultraviolet radiation while supporting overall skin health. These prevention measures can significantly reduce lifetime skin cancer risk when implemented consistently.
Sun protection represents the most important prevention strategy, with daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen being essential regardless of weather conditions or planned activities. Many people underestimate UV exposure during routine activities like driving, walking, or sitting near windows.
Protective clothing provides excellent defense against UV radiation, with tightly woven fabrics, long sleeves, and wide-brimmed hats offering superior protection compared to sunscreen alone. Modern UV-protective clothing combines comfort with highly effective sun protection.
Timing outdoor activities to avoid peak UV hours between 10 AM and 4 PM can dramatically reduce exposure intensity. When midday outdoor time is necessary, seeking shade whenever possible provides additional protection.
Avoiding tanning beds eliminates a significant source of concentrated UV exposure that substantially increases skin cancer risk. No amount of indoor tanning is considered safe, and the cosmetic benefits are far outweighed by the health risks.
Regular skin self-examinations help detect changes early when treatment is most effective. Monthly self-checks using good lighting and mirrors allow individuals to monitor their skin systematically and notice subtle changes over time.
The Art of Self-Examination: Becoming Your Own Health Advocate
Conducting regular skin self-examinations represents one of the most effective tools for early detection of skin cancer and other concerning changes. Learning proper self-examination techniques empowers individuals to take an active role in their health monitoring.
Systematic examination involves checking all skin surfaces in a consistent pattern to ensure complete coverage. This includes areas that don’t receive regular sun exposure, as skin cancer can develop anywhere on the body.
Proper lighting is essential for effective self-examination, with natural daylight providing the best illumination for detecting subtle color changes or irregular textures. Using a hand mirror in combination with a full-length mirror allows examination of difficult-to-see areas.
Photography can be helpful for tracking changes in specific moles or spots over time, providing objective documentation that can assist healthcare providers in evaluating concerning areas.
Involving a partner or family member in skin examinations can help ensure complete coverage of areas that are difficult to see, such as the back, scalp, and back of legs.
Monthly self-examinations establish familiarity with normal skin patterns while creating opportunities to detect changes when they first appear. Consistency in timing and technique improves the effectiveness of self-monitoring.
Professional Screening: When to Seek Expert Evaluation
While self-examination provides valuable ongoing monitoring, professional skin screening by qualified healthcare providers offers expertise in identifying subtle changes that might be missed during self-examination. Understanding when and how often to seek professional evaluation optimizes early detection efforts.
Annual skin examinations by dermatologists are recommended for individuals at high risk due to family history, personal history of skin cancer, or significant sun exposure. These comprehensive examinations use specialized equipment and techniques to identify potentially concerning areas.
Individuals at average risk should discuss appropriate screening intervals with their healthcare providers, as recommendations may vary based on individual circumstances and risk factors.
Professional examination becomes immediately necessary when self-examination reveals changes that meet concerning criteria or when new growths appear that seem different from existing spots.
Dermatoscopy, a specialized technique using magnification and special lighting, allows healthcare providers to examine skin structures not visible to the naked eye, improving diagnostic accuracy for difficult cases.
Documentation during professional examinations creates baseline records that can be compared during future visits to track changes over time and identify areas requiring closer monitoring.
Understanding Biopsy and Diagnostic Procedures
When healthcare providers identify concerning skin changes during examination, various diagnostic procedures may be recommended to determine whether abnormal cells are present. Understanding these procedures helps reduce anxiety and ensures informed decision-making about recommended treatments.
Biopsy procedures involve removing small samples of tissue for microscopic examination by pathologists who specialize in diagnosing cellular abnormalities. Different biopsy techniques are chosen based on the size, location, and characteristics of the concerning area.
Shave biopsies remove surface layers of skin and are commonly used for superficial growths that don’t extend deeply into the skin. This technique typically heals quickly with minimal scarring.
Punch biopsies use circular tools to remove deeper samples of skin and are preferred when the concerning area may extend beyond surface layers. This technique provides more comprehensive tissue samples for analysis.
Excisional biopsies involve complete removal of suspicious areas along with surrounding normal tissue margins. This approach serves both diagnostic and treatment purposes when complete removal is appropriate.
Pathology results typically take several days to over a week, depending on the complexity of the analysis required. Understanding that waiting for results is normal helps manage anxiety during this period.
Treatment Options: From Simple Removal to Advanced Therapies
Treatment for skin cancer and precancerous conditions varies significantly based on the type, size, location, and stage of the condition. Understanding available treatment options helps individuals make informed decisions about their care while maintaining realistic expectations about outcomes.
Surgical excision remains the gold standard for treating most skin cancers, involving complete removal of abnormal tissue along with margins of normal tissue to ensure complete elimination of cancer cells.
Mohs surgery represents a specialized technique that removes skin cancer layer by layer while examining each layer microscopically until clear margins are achieved. This approach maximizes tissue preservation while ensuring complete cancer removal.
Cryotherapy uses extreme cold to destroy abnormal cells and is commonly used for precancerous lesions and some superficial skin cancers. This technique typically heals quickly with minimal scarring.
Topical treatments including prescription creams and gels can effectively treat certain types of precancerous conditions and superficial skin cancers, particularly when multiple lesions are present.
Radiation therapy may be recommended for skin cancers in locations where surgery would be particularly challenging or for individuals who are not good surgical candidates due to other health conditions.
The Role of Technology in Skin Health Monitoring
Advancing technology is revolutionizing skin health monitoring and early detection efforts, providing new tools that enhance both self-examination and professional screening capabilities. Understanding these technological advances helps individuals make informed decisions about incorporating new tools into their skin health routines.
Digital photography and smartphone applications can assist with skin monitoring by providing standardized ways to document and track changes in moles and other skin features over time. However, these tools supplement rather than replace professional evaluation.
Artificial intelligence systems are being developed to assist healthcare providers in analyzing skin images and identifying potentially concerning features. While promising, these technologies currently require human expertise for accurate interpretation.
Dermatoscopy equipment continues to advance, providing increasingly detailed views of skin structures that aid in early detection and accurate diagnosis of various skin conditions.
Telemedicine platforms enable remote consultation with dermatologists, improving access to specialized care particularly for individuals in underserved areas or those with mobility limitations.
Wearable devices that monitor UV exposure help individuals track their daily sun exposure and make informed decisions about protective measures based on actual exposure data.
Lifestyle Factors That Influence Skin Health
Beyond sun protection, numerous lifestyle factors influence overall skin health and cancer risk. Understanding these connections empowers individuals to make choices that support long-term skin health while potentially reducing disease risk.
Nutrition plays a significant role in skin health, with antioxidant-rich foods helping protect against cellular damage while supporting natural repair mechanisms. A balanced diet provides the nutrients necessary for optimal skin function and appearance.
Hydration affects skin health by supporting barrier function and cellular processes. Adequate water intake helps maintain skin moisture and may support the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Sleep quality influences skin repair and regeneration processes that occur during rest periods. Chronic sleep deprivation can impair these processes while increasing stress hormone levels that may negatively impact skin health.
Stress management contributes to skin health by reducing inflammation and supporting immune function. Chronic stress can worsen various skin conditions while potentially interfering with the body’s ability to detect and eliminate abnormal cells.
Exercise provides multiple benefits for skin health including improved circulation, stress reduction, and enhanced immune function. However, outdoor exercise requires careful attention to sun protection to maximize benefits while minimizing risks.
Building a Comprehensive Skin Health Plan
Creating an effective approach to skin health involves integrating prevention strategies, regular monitoring, and professional care into a comprehensive plan that can be maintained long-term. The key is developing sustainable habits that provide ongoing protection and early detection capabilities.
Daily habits including consistent sunscreen use, protective clothing choices, and basic skin care routines form the foundation of effective skin health maintenance. These practices should become automatic parts of daily routines rather than occasional considerations.
Monthly self-examinations provide ongoing monitoring capabilities that complement professional screening efforts. Establishing consistent timing and techniques for self-examination ensures comprehensive coverage and reliable change detection.
Annual professional evaluations by qualified healthcare providers offer expert assessment and early detection capabilities that enhance individual monitoring efforts. These examinations should be scheduled consistently regardless of whether concerning changes have been noticed.
Risk factor modification through lifestyle choices can significantly reduce skin cancer risk while supporting overall health. This includes sun protection, avoiding tanning beds, maintaining healthy nutrition and exercise habits, and managing stress effectively.
Family involvement in skin health awareness benefits everyone by increasing knowledge, supporting consistent preventive practices, and providing assistance with skin monitoring in hard-to-see areas.
Education and Awareness: Spreading the Message
Skin health awareness benefits not only individuals but entire communities when knowledge is shared and preventive practices become cultural norms. Understanding how to effectively communicate about skin health helps create supportive environments for prevention and early detection.
Family education should begin early with age-appropriate discussions about sun safety and skin protection that establish lifelong healthy habits. Children who learn proper sun protection early are more likely to maintain these practices throughout life.
Workplace wellness programs can incorporate skin health education and may be particularly valuable for occupations involving significant sun exposure. Employers benefit from reduced healthcare costs while employees gain valuable health information.
Community education through schools, healthcare facilities, and community organizations helps reach diverse populations with important skin health messages. Culturally appropriate education ensures that all community members receive relevant information.
Advocacy for skin health awareness includes supporting policies that promote sun safety in schools and workplaces while encouraging research into prevention and treatment advances.
Social media and online platforms provide opportunities to share accurate skin health information while countering misinformation that may discourage appropriate prevention or treatment behaviors.
Looking Forward: The Future of Skin Health
Continuing advances in research, technology, and treatment options provide hope for even better outcomes in skin cancer prevention and treatment. Understanding current trends and future directions helps individuals stay informed about emerging opportunities for improved skin health.
Genetic research is revealing new insights about inherited factors that influence skin cancer risk, potentially leading to more personalized prevention and screening recommendations based on individual genetic profiles.
Immunotherapy treatments are showing promise for advanced skin cancers that previously had limited treatment options. These approaches harness the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells more effectively.
Prevention research continues to identify new strategies for reducing skin cancer risk while improving the effectiveness and acceptance of existing prevention measures.
Early detection technologies are becoming more sophisticated and accessible, potentially allowing for earlier identification of concerning changes with greater accuracy.
Global awareness efforts are expanding access to skin health education and services in underserved populations worldwide, potentially reducing the global burden of preventable skin cancers.
Conclusion: Empowering Yourself Through Knowledge
Understanding skin health represents an investment in long-term well-being that pays dividends through reduced disease risk, early detection of problems, and overall confidence in personal health management. The knowledge and tools for effective skin health maintenance are available and accessible to everyone willing to make the commitment to use them consistently.
The key to successful skin health lies in combining daily prevention practices with regular monitoring and appropriate professional care. This comprehensive approach provides multiple opportunities to prevent problems or detect them early when treatment is most effective.
While skin cancer represents a serious health concern, it is largely preventable and highly treatable when detected early. The tools and knowledge for protection and early detection are readily available, making skin cancer one of the most preventable forms of cancer.
Taking control of skin health empowers individuals to protect themselves while serving as advocates for family members and community members who may benefit from increased awareness and education about skin health practices.
The investment of time and effort required for effective skin health maintenance is minimal compared to the potential benefits of prevention and early detection. Making skin health a priority represents one of the most cost-effective health investments anyone can make.